Cabergoline — what it treats and how it helps
Cabergoline is a prescription medicine that lowers prolactin, a hormone made by the pituitary gland. High prolactin can cause missed periods, infertility, low sex drive, milk production when you aren’t pregnant, and symptoms from pituitary tumors called prolactinomas. For many people, cabergoline reduces prolactin quickly and can shrink these tumors without surgery.
How cabergoline works and when it's used
Cabergoline is a dopamine agonist. That means it mimics dopamine, which tells the pituitary to stop making prolactin. Doctors commonly prescribe it for:
- Hyperprolactinemia (high prolactin levels)
- Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas (prolactinomas)
- Sometimes to stop unwanted milk production after delivery or in specific fertility plans (only under close medical advice)
It’s usually given as a pill taken once or twice a week. Typical starting dose is 0.25 mg twice weekly or 0.5 mg once weekly, and doctors adjust the dose based on blood tests and symptoms. Never change the dose without checking with your prescriber.
Safety, side effects, and practical tips
Common side effects are nausea, headache, dizziness, tiredness, constipation, and low blood pressure when standing (orthostatic hypotension). These usually improve after a few weeks. To reduce nausea, take the pill with food and avoid standing up quickly.
Less common but important risks include heart valve problems (mainly at higher doses used for Parkinson’s), psychiatric effects like impulse control issues (e.g., gambling or unusual behavior), and fainting. If you notice shortness of breath, chest pain, fainting, sudden mood or behavior changes, tell your doctor right away.
Before starting cabergoline, your doctor will usually check prolactin levels and discuss heart and mental health history. If you take high doses long term, an echocardiogram (heart ultrasound) may be recommended to watch for valve changes.
Drug interactions to watch for: medications that block dopamine (certain antipsychotics) can reduce cabergoline’s effect. Combining cabergoline with other drugs that lower blood pressure can increase dizziness. Always give your full medication list to the prescriber, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Practical tips: take a pregnancy test before starting and use reliable contraception if you’re not planning pregnancy; discuss breastfeeding plans with your doctor. Don’t drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how cabergoline affects you. Keep regular blood tests to track prolactin and follow-up imaging if you have a tumor.
If you have questions about dosing, side effects, or monitoring, ask your prescribing clinician. Cabergoline works well for many people, but the best results come from careful follow-up and honest communication with your healthcare team.
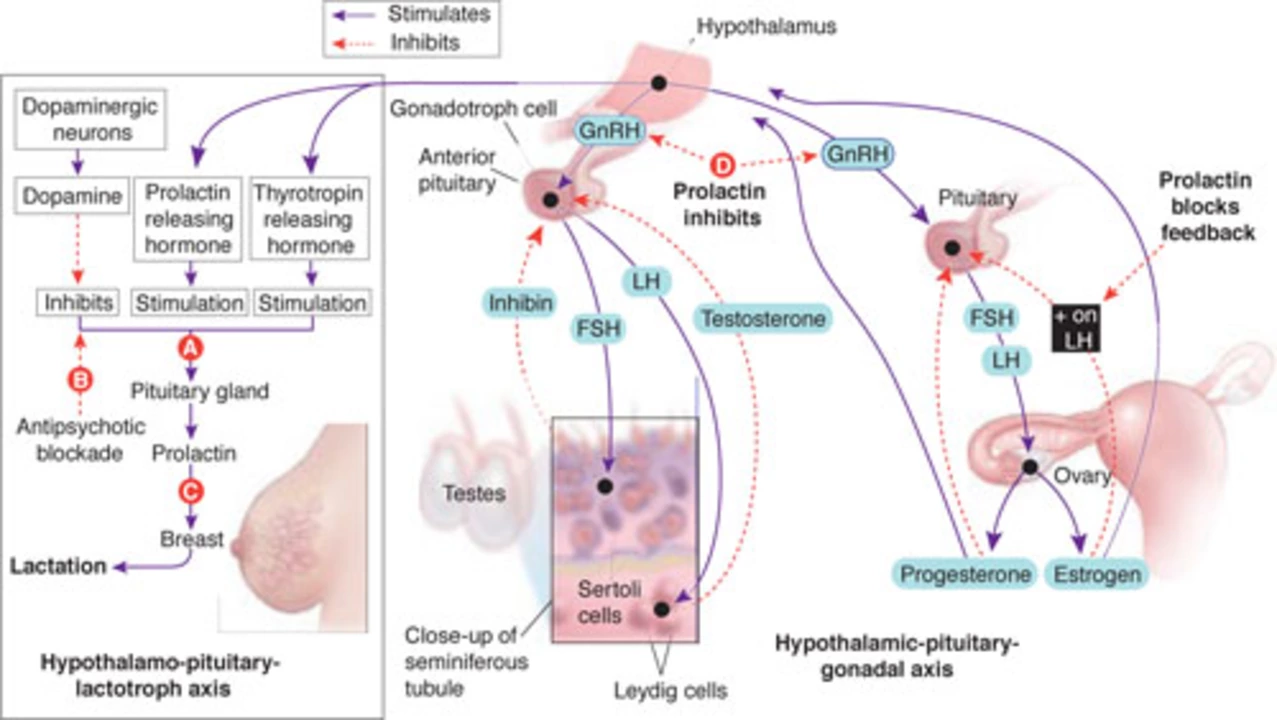
Managing Hyperprolactinemia: The Role of Cabergoline
In my recent research on managing Hyperprolactinemia, I discovered the important role of a medication called Cabergoline. Hyperprolactinemia is a condition where the body produces too much prolactin hormone, leading to various health issues. Cabergoline works by reducing the production of prolactin, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve overall health. Many patients have found relief through this medication, allowing them to live a more normal life. I believe it's essential to spread awareness about Cabergoline and its effectiveness in managing Hyperprolactinemia.
read more