Anticoagulants: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your blood clots too much, it can lead to strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolisms. That’s where anticoagulants, medications that slow down the blood’s ability to form clots. Also known as blood thinners, they don’t actually thin your blood—they just make it harder for dangerous clots to form. If you’ve ever been told you need one after surgery, for atrial fibrillation, or after a deep vein thrombosis, you’re not alone. Millions use them every year to stay safe.
Not all anticoagulants work the same way. Some, like warfarin, an older oral anticoagulant that blocks vitamin K, need regular blood tests to keep doses right. Others, like heparin, a fast-acting injectable often used in hospitals, work quickly but don’t last long. Newer options like rivaroxaban and apixaban don’t need constant monitoring, but they’re pricier. Each has trade-offs: cost, convenience, risk of bleeding, and how they interact with food or other drugs. You can’t pick one blindly—your doctor has to match it to your body, your lifestyle, and your health history.
What you won’t find in most brochures? How often people mix them with NSAIDs or herbal supplements and end up in the ER. Or why some folks on warfarin suddenly start bruising after eating more kale. These aren’t rare cases—they’re everyday risks. The posts below cover real stories and real science: how anticoagulants interact with antibiotics, how to track safety alerts from the FDA, and what to do when side effects show up. You’ll also see comparisons with other drugs, like how blood pressure meds can accidentally make clotting worse, or how weight changes affect how these drugs work in your system. This isn’t theory. It’s what people actually deal with when they’re taking these pills every day.
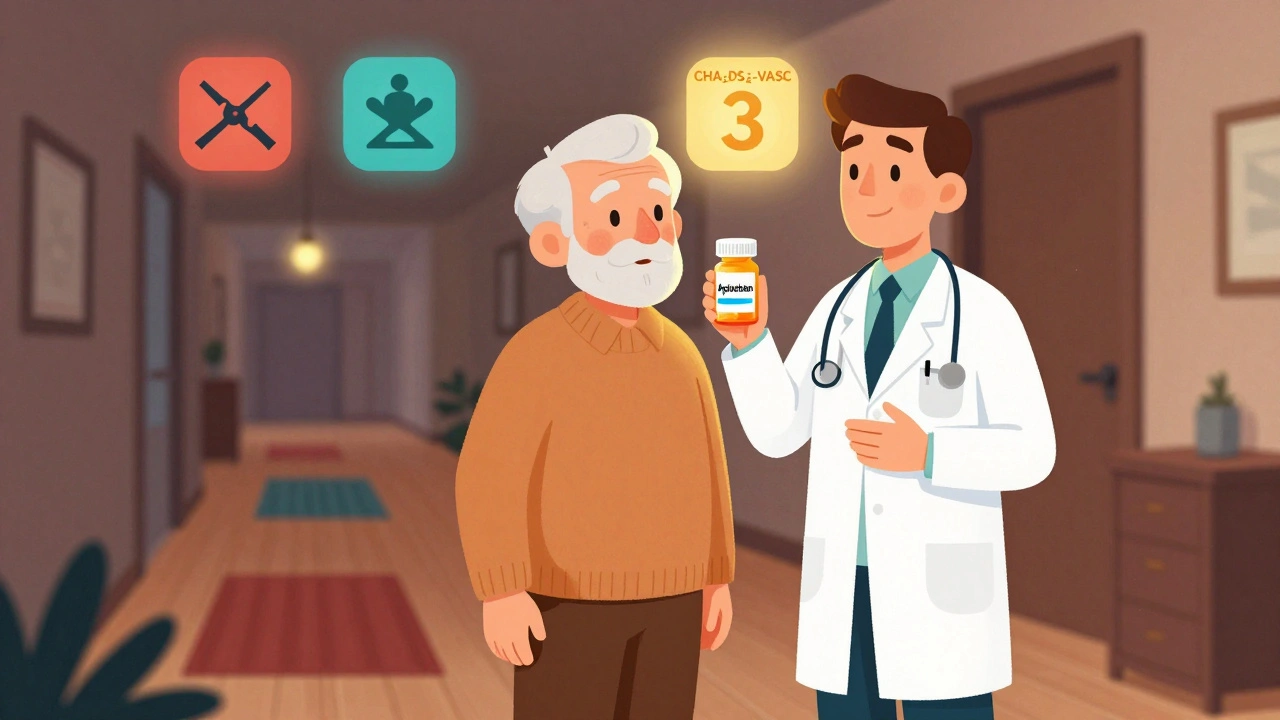

Falls Risk on Anticoagulants: How to Prevent Bleeding Without Stopping Blood Thinners
Falls shouldn't stop you from taking blood thinners. Learn why stopping anticoagulants for fall risk increases stroke danger-and how DOACs, fall prevention, and proper risk scores can keep you safe without compromising protection.
read more
Cosmetic Procedures and Anticoagulants: What You Need to Know About Bruising and Bleeding Risks
Learn the truth about blood thinners and cosmetic procedures: stopping them can be more dangerous than keeping them. Find out which medications are safe to continue and what procedures carry real risks.
read more