Understanding Diabetes Type 2 and Thyroid Disorders
As someone who always keeps an eye on health-related topics, I've noticed that there's a significant connection between diabetes type 2 and thyroid disorders. In this article, I want to share with you what I've learned about these conditions and why it's essential to be aware of the link between them. I hope that by the end of this article, you'll have a better understanding of how these disorders are connected and what you can do to manage them effectively.
The Basics of Diabetes Type 2 and Thyroid Disorders
Before diving into the connection between diabetes type 2 and thyroid disorders, let's take a moment to understand what these conditions are. Diabetes type 2 is a chronic disease that affects the way your body processes glucose (sugar). People with this condition either don't produce enough insulin or have insulin resistance, meaning their cells don't respond well to insulin. This results in high blood sugar levels, which can lead to various health complications.
On the other hand, thyroid disorders are conditions that affect the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. This gland produces hormones that regulate your body's metabolism, growth, and development. Thyroid disorders can either cause the gland to produce too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or not enough (hypothyroidism). Both conditions can impact your overall health and well-being.
The Link Between Diabetes Type 2 and Thyroid Disorders
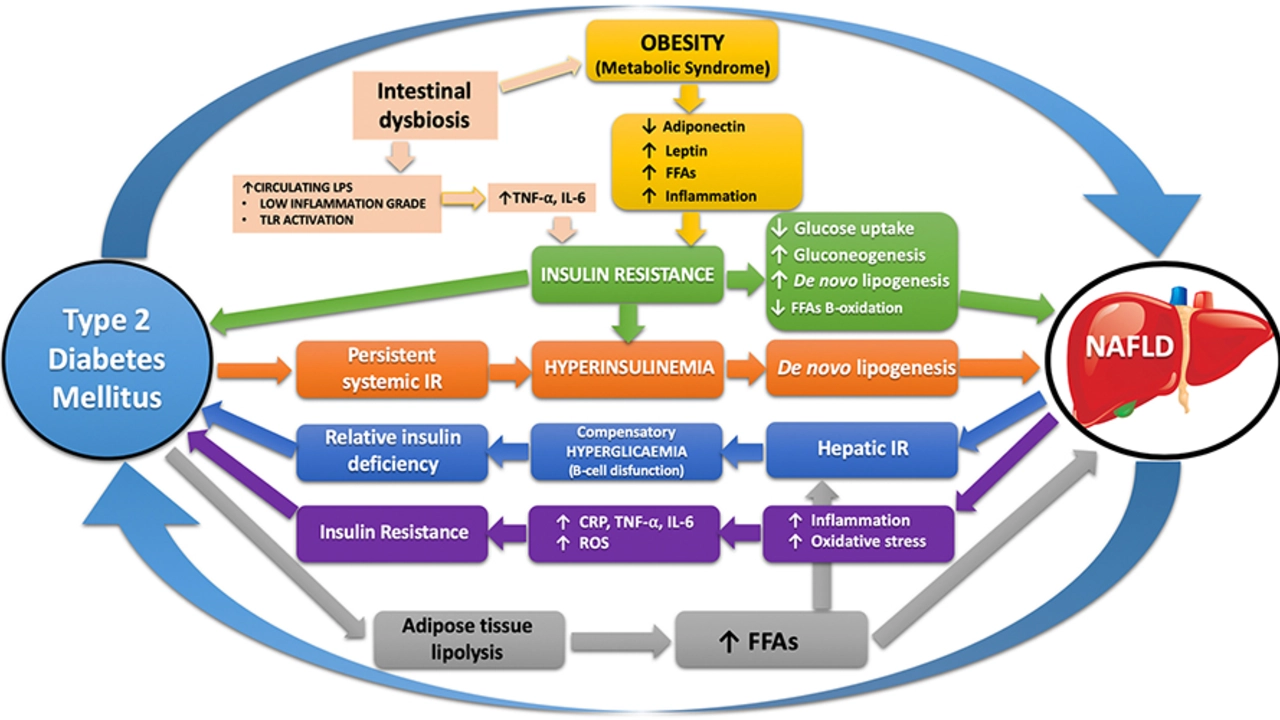
Now that we have a basic understanding of these conditions, let's explore the connection between them. Several studies have shown that people with diabetes type 2 are more prone to develop thyroid disorders, particularly hypothyroidism. The reasons behind this connection are still not fully understood, but it's believed that both conditions share some common risk factors, such as genetics, obesity, and autoimmune diseases.
Moreover, thyroid hormones can influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which can impact blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. And in turn, uncontrolled diabetes can affect thyroid function, creating a vicious cycle that can exacerbate both conditions if not properly managed.
How Diabetes Affects Thyroid Function
As I mentioned earlier, diabetes can directly impact thyroid function. High blood sugar levels can lead to a state of low-grade inflammation in the body, which can negatively affect the thyroid gland. This inflammation can cause the thyroid gland to produce less hormone, leading to hypothyroidism.
Additionally, insulin resistance, which is a common issue in people with diabetes type 2, can also contribute to thyroid dysfunction. Insulin resistance can lead to higher levels of circulating insulin, which can stimulate the thyroid gland to grow and produce more hormones, resulting in hyperthyroidism in some cases.
Thyroid Disorders and Diabetes Management
Since thyroid disorders can impact blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, it's crucial for people with diabetes to regularly monitor their thyroid function. If you have diabetes and are diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, your healthcare provider may need to adjust your diabetes management plan to account for the changes in your thyroid function.
For example, if you have hypothyroidism, you may require higher doses of insulin or other diabetes medications to maintain proper blood sugar levels. Conversely, if you have hyperthyroidism, you may need lower doses of medication, as your body becomes more sensitive to insulin.
Managing Thyroid Disorders in People with Diabetes
If you have both diabetes and a thyroid disorder, it's essential to address both conditions to maintain your overall health. For hypothyroidism, your healthcare provider may prescribe synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which can help regulate your thyroid hormone levels and improve your insulin sensitivity.
For hyperthyroidism, treatment options may include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. It's important to work closely with your healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for your specific situation.
Preventing Thyroid Disorders in People with Diabetes
While it may not be possible to completely prevent thyroid disorders in people with diabetes, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, can help support your thyroid function and overall health.
Additionally, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and routine blood tests to monitor your thyroid function can help detect any potential issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and management of both your thyroid disorder and diabetes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between diabetes type 2 and thyroid disorders is an important one that should not be overlooked. By understanding the link between these conditions and taking steps to manage and prevent them, you can improve your overall health and well-being. Remember to always work closely with your healthcare provider to develop the best treatment plan for your specific needs.

19 Comments
If you think you can dodge the thryoid‑diabetes link, think again. The overlap of insulin resistance and thyroid hormone production is well‑documented, and ignoring it only worsens outcomes.
Metabolic crosstalk amplifies endocrine dysregulation, yielding a feedback loop of insulin resistance and thyroid hormone imbalance.
Understanding how hyperglycemia can trigger low‑grade inflammation that impairs thyroid function is essential for anyone managing type‑2 diabetes. Addressing both conditions simultaneously often leads to better glycemic control and fewer complications.
It’s fascinating how the body’s regulatory networks mirror philosophical paradoxes-each system striving for balance yet constantly perturbed by the other’s fluctuations.
Consider integrating a Mediterranean‑style diet rich in omega‑3 fatty acids; it supports insulin sensitivity while also nurturing thyroid health. Adding selenium‑rich foods like Brazil nuts can further boost hormone conversion.
Don’t be fooled-big pharma doesn’t want you to know that the same meds that mask diabetes symptoms can also silence thyroid warnings. Keep an eye on your labs, they’re trying to keep you in the dark.
When you’re juggling medication schedules, the key is consistency. Take your thyroid hormone at the same time each morning, ideally on an empty stomach, and monitor blood sugar trends closely after any dosage change.
Data‑driven adherence strategies, such as electronic pill trackers, can quantify the impact of timing on both insulin and levothyroxine efficacy, reducing variability in clinical outcomes.
Great reminder! 🌟 Keeping both systems in check is a marathon, not a sprint, and every small habit adds up! 😊
Let’s rally the community: share your success stories of synchronized diabetes‑thyroid management, and we’ll build a resource pool that fuels motivation for everyone.
From a cultural perspective, many traditional cuisines already incorporate iodine‑rich seaweed and whole‑grain staples, which can naturally support thyroid function while controlling glycemic spikes.
The interplay between type‑2 diabetes mellitus and thyroid pathology represents a multifaceted endocrine nexus that extends beyond mere coincidence.
The epidemiological surveys consistently reveal a higher prevalence of hypothyroidism among diabetic cohorts, suggesting shared pathogenic mechanisms.
One pivotal mechanism involves chronic hyperinsulinemia, which can alter deiodinase activity, thereby modulating peripheral conversion of T4 to the active T3 hormone.
Conversely, inadequate thyroid hormone levels impair hepatic glucose output, exacerbating insulin resistance and fostering a vicious metabolic loop.
Genetic predisposition also contributes, as polymorphisms in the TSH receptor and PPAR‑γ genes have been implicated in both conditions.
Moreover, autoimmune dysregulation, typified by the presence of anti‑thyroid peroxidase antibodies, frequently co‑exists with the inflammatory milieu of adipose tissue in obesity‑related diabetes.
Clinicians should therefore adopt a bidirectional screening approach, measuring serum TSH and free T4 alongside HbA1c during routine assessments.
Early detection permits timely initiation of levothyroxine therapy, which has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in several controlled trials.
Adjustment of antidiabetic regimens may also be necessary, as thyroid hormone replacement can alter the pharmacokinetics of sulfonylureas and insulin analogs.
Patient education is paramount; individuals must understand that symptom overlap-such as fatigue and weight fluctuation-requires careful clinical interpretation.
Lifestyle interventions, including weight reduction through calibrated aerobic exercise, simultaneously attenuate insulin resistance and support optimal thyroid hormone utilization.
Nutritional adequacy, particularly adequate iodine and selenium intake, further sustains endocrine homeostasis.
Regular follow‑up appointments enable dynamic dose titration, preventing iatrogenic hyperthyroidism, which itself can precipitate hyperglycemic excursions.
Interdisciplinary collaboration between endocrinologists, primary care physicians, and diabetes educators enhances coordinated care delivery.
Future research should aim to elucidate the molecular crosstalk pathways, potentially unveiling novel therapeutic targets that address both disorders concurrently.
In summary, recognizing and managing the bidirectional relationship between type‑2 diabetes and thyroid dysfunction is essential for reducing morbidity and improving quality of life.
Wow this info is solid 👍 keep sharing more tips 😂
Hey folks, just wanted to say thanks for the practical advice – it’s really helped me keep my labs in check :)
Thyroid health isn’t a side quest it’s central to metabolic balance. Keep an eye on TSH especially if you’re on insulin. Simple tweaks can make a huge difference.
Synchronize medication timing to avoid absorption competition.
Oh great, another “holistic” guru telling us to eat kale while pharma keeps us chained to pills. Wake up.
Dont forget to ask your doc about thryoid screening when you get your diabetes check‑up.
Hey love your post keep it up!