Hyperprolactinemia: What High Prolactin Looks Like and How to Handle It
High prolactin levels (hyperprolactinemia) show up in different ways. Some people notice milk production when they aren’t pregnant or breastfeeding, irregular periods, or trouble getting pregnant. Men may see lowered libido, erectile problems, or breast growth. Sometimes there are no obvious symptoms and a routine blood test finds it.
What causes high prolactin?
Several things can raise prolactin. A small pituitary tumor called a prolactinoma is common. Certain medicines — especially some antipsychotics, metoclopramide (a nausea drug), and high-dose antidepressants — can push levels up. Other causes include low thyroid function, chest wall irritation (from surgery or tight clothing), stress, and pregnancy. Rarely, other pituitary problems or kidney disease play a role.
One tricky issue is macroprolactin, a large, inactive form of prolactin that can give a high lab result but usually doesn’t cause symptoms. If your levels don’t match how you feel, ask your doctor to test for macroprolactin.
How it’s diagnosed and treated
If a blood test shows high prolactin, doctors usually repeat it in the morning and check thyroid function. If levels are clearly high, an MRI of the pituitary gland is the next step to look for a prolactinoma. Treatment depends on the cause, how high the number is, and symptoms.
For prolactinomas, the first-line drugs are dopamine agonists — cabergoline and bromocriptine. They lower prolactin, shrink tumors, and often restore normal periods and sex drive. Side effects can include nausea, dizziness, or low blood pressure when standing; many people tolerate these medicines well. If a medication you take is the cause, your doctor may switch it or adjust the dose instead of stopping it on your own.
If a pituitary tumor is large or doesn’t respond to medicine, surgical removal may be needed. If hypothyroidism is the reason, treating the thyroid usually brings prolactin down. For mild or asymptomatic cases, your doctor might recommend watchful waiting with periodic blood tests and imaging.
Simple actions you can take now: avoid tight chest pressure, review current meds with your provider, and don’t stop prescribed drugs suddenly. Keep a record of symptoms — menstrual changes, sexual changes, nipple discharge — and share them with your clinician.
When to see a specialist: sudden vision changes, severe headaches, persistent nipple discharge, or trouble conceiving. An endocrinologist can map out the right tests and treatment. With proper diagnosis and care, most causes of high prolactin are treatable and symptoms improve.
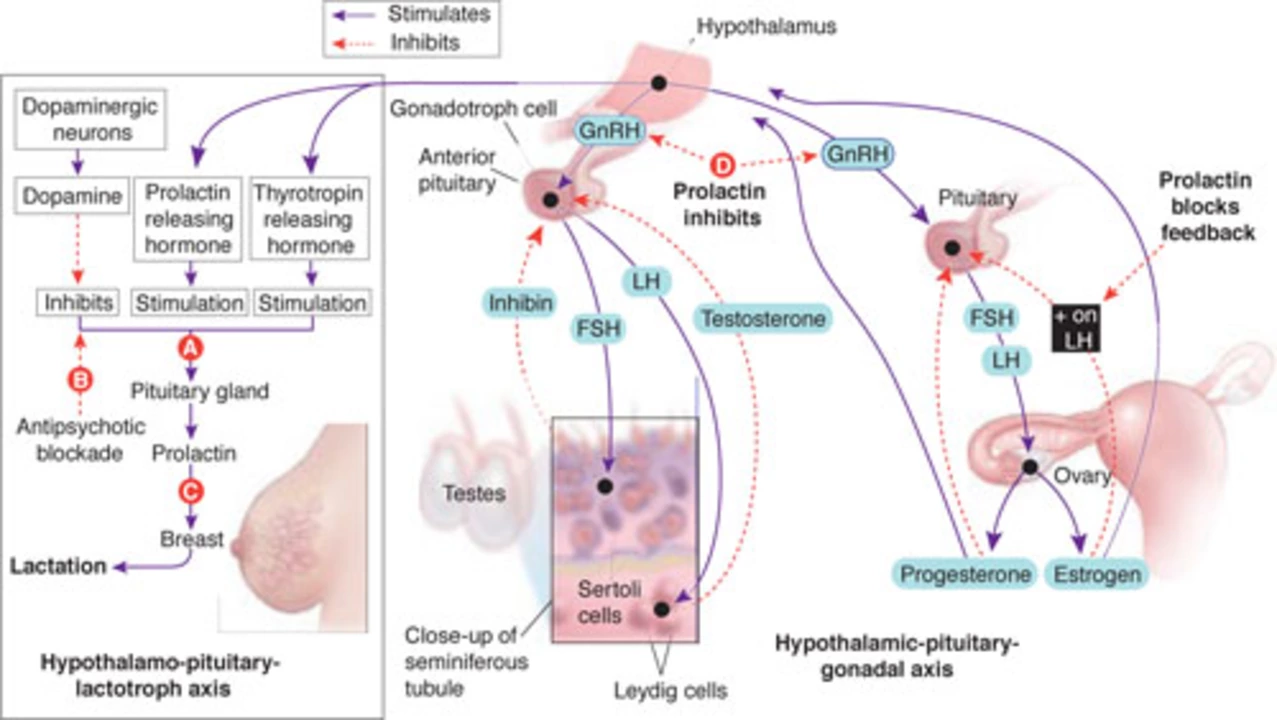
Managing Hyperprolactinemia: The Role of Cabergoline
In my recent research on managing Hyperprolactinemia, I discovered the important role of a medication called Cabergoline. Hyperprolactinemia is a condition where the body produces too much prolactin hormone, leading to various health issues. Cabergoline works by reducing the production of prolactin, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve overall health. Many patients have found relief through this medication, allowing them to live a more normal life. I believe it's essential to spread awareness about Cabergoline and its effectiveness in managing Hyperprolactinemia.
read more